Customized Robotic Automation
The manufacturing industry has undergone a remarkable transformation with the advent of customized robotic automation. This technology has revolutionized traditional manufacturing processes by incorporating advanced robotic systems tailored to specific tasks and requirements. In this article, we will explore the myriad benefits of customized robotic automation and its significance.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity Customized robotic automation offers unparalleled efficiency and productivity gains in the manufacturing industry. Robots can perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks with remarkable speed, accuracy, and consistency, surpassing human capabilities when compared on an hour by hour day by day basis. By automating these tasks, manufacturers can significantly reduce production cycle times and increase overall output, leading to improved productivity levels.
Moreover, customized robots can be designed to work collaboratively with human operators, complementing their skills and abilities. This human-robot collaboration creates a harmonious work environment, where robots handle repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex and value-added activities where dexterity is crucial and training of robots is laborious or the costly end effectors simply not viable. As a result, employees can utilize their expertise and creativity to drive innovation and enhance the overall manufacturing process.
Increased Efficiency and Productivity Customized robotic automation offers unparalleled efficiency and productivity gains in the manufacturing industry. Robots can perform repetitive and labor-intensive tasks with remarkable speed, accuracy, and consistency, surpassing human capabilities when compared on an hour by hour day by day basis. By automating these tasks, manufacturers can significantly reduce production cycle times and increase overall output, leading to improved productivity levels.
Moreover, customized robots can be designed to work collaboratively with human operators, complementing their skills and abilities. This human-robot collaboration creates a harmonious work environment, where robots handle repetitive tasks, allowing humans to focus on more complex and value-added activities where dexterity is crucial and training of robots is laborious or the costly end effectors simply not viable. As a result, employees can utilize their expertise and creativity to drive innovation and enhance the overall manufacturing process.
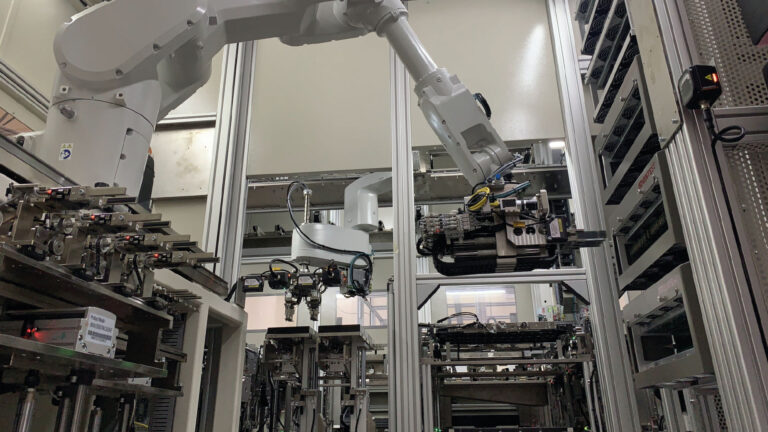

Enhanced Quality and Precision
Quality control is paramount in the manufacturing industry, and customized robotic automation plays a crucial role in ensuring consistent and precise production. Robots are programmed to execute tasks with unparalleled accuracy, minimizing errors and defects. By eliminating human error, manufacturers can achieve exceptional levels of product quality and consistency over a full 24 hour work day, which enhances customer satisfaction, brand reputation and the bottom line.
Furthermore, customized robotic automation enables real-time monitoring and data collection, facilitating comprehensive quality control and process optimization. Sensors and cameras integrated into the robotic systems can detect even the tiniest variations or anomalies, enabling immediate corrective actions. Manufacturers can also analyze the collected data to identify patterns, detect potential issues, and make informed decisions to further improve product quality. Today with initiatives like I4.0 and CFX it is possible for the data sets to be shared and upstream processes changed based on downstream experiences in the assembly line.
Furthermore, customized robotic automation enables real-time monitoring and data collection, facilitating comprehensive quality control and process optimization. Sensors and cameras integrated into the robotic systems can detect even the tiniest variations or anomalies, enabling immediate corrective actions. Manufacturers can also analyze the collected data to identify patterns, detect potential issues, and make informed decisions to further improve product quality. Today with initiatives like I4.0 and CFX it is possible for the data sets to be shared and upstream processes changed based on downstream experiences in the assembly line.
Size and Scope from Semicon to Strawberries
Automation has no bounds when considering its “Industrial Fit”, it has revolutionized industries, from semiconductor manufacturing to food production adding efficiency, accuracy, and productivity. In the semiconductor industry, automation plays a crucial role in the fabrication process. Advanced robotic systems are employed for tasks like wafer handling, equipment maintenance, and quality control, reducing human error and enhancing throughput. Robot systems are inherently clean and ironically humans are not, so the finest, most advanced electronics benefit from as little human contact as possible.
In the automotive sector, automation has transformed assembly lines, enabling rapid production and customization, performing repetitive tasks with precision and speed, resulting in improved product quality and reduced costs. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, automation has streamlined drug manufacturing, ensuring precise dosage formulations, reducing contamination risks, and accelerating production timelines.
In the food production sector automated sorting systems efficiently categorize fruits, vegetables, and grains based on size, color, and quality, optimizing the production line. Food packaging processes are automated, ensuring consistent packaging and reducing waste. Additionally, robotic systems are utilized for tasks like slicing, dicing, and food handling, enhancing food safety standards and increasing production capacity.
Automation has also found applications in logistics and warehousing. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) navigate warehouses, transporting goods with minimal human intervention. This improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes errors in order fulfillment. Amazon and E commerce in general would not be the industry it has become without automation and robotics.
As technology continues to advance, the potential for automation in different sectors continues to expand, leading to further optimization and advancements in diverse industries.
In the automotive sector, automation has transformed assembly lines, enabling rapid production and customization, performing repetitive tasks with precision and speed, resulting in improved product quality and reduced costs. Similarly, in the pharmaceutical industry, automation has streamlined drug manufacturing, ensuring precise dosage formulations, reducing contamination risks, and accelerating production timelines.
In the food production sector automated sorting systems efficiently categorize fruits, vegetables, and grains based on size, color, and quality, optimizing the production line. Food packaging processes are automated, ensuring consistent packaging and reducing waste. Additionally, robotic systems are utilized for tasks like slicing, dicing, and food handling, enhancing food safety standards and increasing production capacity.
Automation has also found applications in logistics and warehousing. Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) navigate warehouses, transporting goods with minimal human intervention. This improves operational efficiency, reduces costs, and minimizes errors in order fulfillment. Amazon and E commerce in general would not be the industry it has become without automation and robotics.
As technology continues to advance, the potential for automation in different sectors continues to expand, leading to further optimization and advancements in diverse industries.
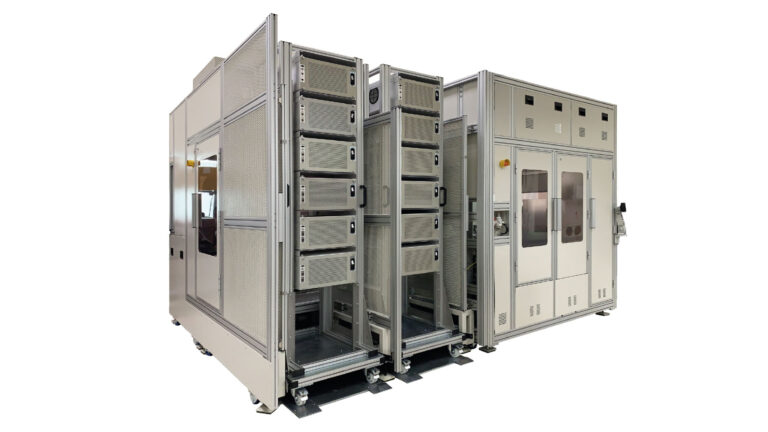

Flexible and Scalable Production
One of the key advantages of customized robotic automation is its flexibility and scalability. Unlike traditional fixed automation systems, customized robots can be easily reprogrammed and reconfigured to adapt to changing manufacturing requirements. This agility allows manufacturers to respond swiftly to market demands, introduce new products, or modify existing ones with minimal downtime and retooling costs. When machine life maybe measured as 7 to 10 years or longer but product life times measured in a year or two – the capital outlay for automation must include a capability for upgrading or retooling else the first product alone may not justify the expense.
Customized robotic automation also enables manufacturers to scale their production capabilities efficiently. As demand increases or fluctuates, additional robots can be seamlessly integrated into the production line, allowing for increased output and faster turnaround times, or capacity can be “turned off” until it is needed without the issues associated to layoffs. When the market recovers that capacity can quickly be brought back online.
Additionally – recruitment in the manufacturing industry today poses several challenges. Manufacturing jobs often suffer from a negative perception, seen as physically demanding and lacking career growth opportunities. This deters potential applicants, exacerbating the talent shortage with competition for skilled workers being fierce, with other industries offering attractive alternatives. Lastly, the aging manufacturing workforce creates a looming retirement wave, intensifying the need for new talent. Automation plays a significant role in allowing companies to predictable growth in an environment where labor shortages may prevail. The ability to employ robots for as much as 24 hours a day with limited human participation at a unit cost that drops the more hours they are employed changes the financial model of 1, 2 or 3 shifts of old. In many manufacturing plants it was common for output and quality to vary significantly between first and third shifts and costs to vary accordingly. With a robotic line, both quality and cost can be predicted. This scalability ensures that manufacturers can meet customer demands promptly while maintaining high levels of efficiency and quality.
Customized robotic automation also enables manufacturers to scale their production capabilities efficiently. As demand increases or fluctuates, additional robots can be seamlessly integrated into the production line, allowing for increased output and faster turnaround times, or capacity can be “turned off” until it is needed without the issues associated to layoffs. When the market recovers that capacity can quickly be brought back online.
Additionally – recruitment in the manufacturing industry today poses several challenges. Manufacturing jobs often suffer from a negative perception, seen as physically demanding and lacking career growth opportunities. This deters potential applicants, exacerbating the talent shortage with competition for skilled workers being fierce, with other industries offering attractive alternatives. Lastly, the aging manufacturing workforce creates a looming retirement wave, intensifying the need for new talent. Automation plays a significant role in allowing companies to predictable growth in an environment where labor shortages may prevail. The ability to employ robots for as much as 24 hours a day with limited human participation at a unit cost that drops the more hours they are employed changes the financial model of 1, 2 or 3 shifts of old. In many manufacturing plants it was common for output and quality to vary significantly between first and third shifts and costs to vary accordingly. With a robotic line, both quality and cost can be predicted. This scalability ensures that manufacturers can meet customer demands promptly while maintaining high levels of efficiency and quality.
Improved Workplace Safety
Workplace safety is a paramount concern in any manufacturing environment. Customized robotic automation significantly enhances safety by reducing human exposure to hazardous and physically demanding tasks. Robots can handle tasks involving heavy lifting, repetitive motions, or exposure to harmful substances, minimizing the risk of injuries and accidents.
By automating high-risk processes, manufacturers can create a safer working environment for their employees. Robots are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features, enabling them to detect and respond to potential dangers promptly. Collaborative robots, designed to work alongside humans, are equipped with sensitive force sensors that can detect human presence and adjust their movements accordingly, ensuring a safe and harmonious interaction.
By automating high-risk processes, manufacturers can create a safer working environment for their employees. Robots are equipped with advanced sensors and safety features, enabling them to detect and respond to potential dangers promptly. Collaborative robots, designed to work alongside humans, are equipped with sensitive force sensors that can detect human presence and adjust their movements accordingly, ensuring a safe and harmonious interaction.
Socioeconomic Considerations
The increased use of automation brings forth a range of risks to employment. While automation undoubtedly offers numerous benefits such as improved productivity, efficiency, and cost reduction, it also poses challenges for the workforce and Industrial leaders should continue to recognize they have a responsibility for all stake holders not simply shareholders.
- Job displacement: Automation can replace human workers by performing tasks more efficiently and cost-effectively leading to a risk of job losses for workers involved in those tasks. Roles such as assembly line workers, machine operators, and quality inspectors may be particularly vulnerable.
- Skills mismatch: The transition to automated manufacturing processes demands a shift in the skills required for the workforce. As new technologies and systems are implemented, workers need to acquire new technical skills to remain relevant in the job market. However, there may be a skills mismatch between the abilities of existing workers and the demands of automated manufacturing, leading to job insecurity.
- Unequal impact: The risks associated with automation are not evenly distributed across all workers. Low-skilled and routine-based jobs are more susceptible to automation, while higher-skilled and knowledge-intensive roles may see less impact. This disparity can exacerbate income inequality and socioeconomic divisions, as certain groups are disproportionately affected by job losses.
- Workforce restructuring: Automation often necessitates a reconfiguration of the workforce. While some workers may be retrained to operate and maintain automated systems, others may need to transition into different roles or industries. This restructuring process can be challenging, requiring significant investments in retraining and upskilling programs, and some individuals may struggle to adapt to new employment opportunities.
- Economic implications: Automation can have broader economic consequences. Job losses in manufacturing may result in reduced consumer spending power, impacting other industries that rely on consumer demand. Additionally, communities heavily dependent on manufacturing jobs may face significant economic disruptions, leading to localized unemployment and social issues.
- Ethical considerations: As automation replaces human labor, questions arise regarding the ethical implications of this shift. The social and psychological impacts of job loss, the potential erosion of worker rights, and the implications for overall societal well-being require careful consideration and proactive measures to mitigate potential negative effects.
- Addressing these risks requires a multifaceted approach. Governments, businesses, and educational institutions need to collaborate to ensure effective retraining and reskilling programs, promote lifelong learning initiatives, and establish policies that facilitate a smooth transition for affected workers. Additionally, efforts should be made to identify new job opportunities created by automation and to foster entrepreneurship and innovation to drive economic growth and job creation.
Conclusion
Customized robotic automation has ushered in a new era of efficiency, precision, flexibility, and safety in the manufacturing industry. By leveraging tailored robotic solutions, manufacturers can achieve unprecedented levels of productivity, superior product quality, and adaptability to changing market demands. Embracing customized robotic automation is no longer a choice but a necessity for manufacturers striving to stay competitive in an increasingly dynamic and demanding global market.